
Reverse osmosis systems are a comprehensive water treatment method that can be used at home or for large industrial applications. Because of the effectiveness of the reverse osmosis membrane., they offer a more advanced treatment process than simple home systems, such as refrigerator filters, under-sink carbon filters, or water pitcher filters. However, multiple other filters are at play in a reverse osmosis system. The configuration of these other filters is what makes each RO system unique, providing the consumer with customization options. In this article, you can learn more about the different stages of reverse osmosis systems and how they work.
Why do reverse osmosis systems have different numbers of stages?The stages of reverse osmosis systems determine the makeup of the treated water. They allow you to customize your system to output the desired water quality you want. For example, a 5-stage system will incorporate more carbon filters than a 3-stage system, effectively removing more chlorine, chloramines, foul tastes, and odors than the 3-stage system. If you want to add back beneficial minerals to water, you will want a system that incorporates a remineralization cartridge as the fourth or fifth stage. The number of stages in a system determine factors, such as size of the system, maintenance expenses, and overall system price.
How many stages should my RO system have?When deciding which RO system to purchase, consider the following questions:
- How many stages does the RO system contain? Generally, the more stages an RO system has, the higher quality the output water will be. Compared to many common home water filters, however, a 3-stage and 5-stage RO system both output high quality water.
- Will the system fit under my sink? The number of stages an RO system contains will affect the size of the system. Ensure that you have the space for a larger system if that is the type of system you choose.
- Does the system contain any additional features I want? These features could look like a remineralization cartridge, permeate pump, or an easy method of cartridge replacement.
- How expensive are cartridge replacements? The more stages you have in your RO system, the more cartridges you will need to purchase on a regular basis. If you choose a system with proprietary cartridges, these will also be more expensive than standard cartridge replacements.
Learn more: 6 must-have reverse osmosis features
Reverse osmosis configurationsA typical 3-stage RO system contains a sediment prefilter, carbon prefilter, and a reverse osmosis membrane. The first stage, the sediment filter, removes dirt and debris before water travels to the carbon filter and membrane. The carbon filter effectively removes a majority of chlorine, chloramines, foul tastes, and odors, but there will always be some residual contaminants. If you want your system to contain two carbon filters, you will need a 4-stage system that includes a secondary carbon prefilter or postfilter. Instead of a second carbon filter, some 4-stage systems contain a remineralization postfilter. This adds beneficial minerals back to the water after they have been removed by the RO membrane. A 5-stage reverse osmosis system may contain an additional carbon prefilter or a remineralization cartridge.
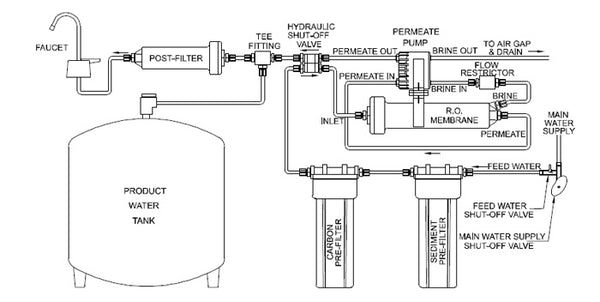
3-stage reverse osmosis system configuration
A 3-stage RO system may contain a sediment prefilter, carbon prefilter, and RO membrane. A common configuration involves a dual carbon-sediment prefilter, RO membrane, and a carbon postfilter. This configuration allows for multiple levels of carbon filtration while also removing sediment with only 3 stages.
- Carbon/sediment prefilter: An activated carbon prefilter reduces elements that cause water to taste and smell unpleasant, like chlorine. The carbon prefilter removes chlorine to protect the RO membrane. A dual carbon-sediment prefilter provides the benefits of carbon filtration while also removing sediment, dirt, and other debris.
- RO membrane: The RO membrane filters out dissolved solids, including radium, lead, arsenic, and many others. The membrane is the heart of the RO system as it removes the contaminants most other treatment methods cannot. The flow rate of the membrane determines how much water an RO system can output in a day.
- Polishing carbon postfilter: Stage 3 is a second activated carbon filter that polishes the water to make sure it's crystal clear.
4-stage reverse osmosis system configuration
A typical 4-stage RO system contains a sediment prefilter, carbon prefilter, RO membrane, and a polishing carbon postfilter.
- Sediment prefilter: A sediment prefilter screens out dirt, sand, rust, and other microscopic particles 15 times smaller than a grain of sand.
- Carbon prefilter: An activated carbon prefilter reduces elements that cause water to taste and smell unpleasant, including chlorine.
- RO membrane: The RO membrane filters out dissolved substances, including radium, lead, arsenic, and many others.
- Polishing carbon filter: The polishing filter is a second activated carbon filter that polishes the water to make sure it's crystal clear.
Some 4-stage RO systems, such as the Neo-Pure PRO-4 Series, use a remineralization cartridge to add beneficial minerals back to water. These configurations look like the following:
- Dual carbon-sediment prefilter: A sediment and carbon filter provides the benefits of each filter type.
- RO membrane: The RO membrane removes all the hard to remove contaminants that carbon and sediment cannot.
- Polishing carbon filter: The polishing carbon filter removes any remaining foul tastes and odors that the prefilter may have missed.
- Remineralization cartridge: The remineralization cartridge adds beneficial minerals that were removed by the RO membrane. Because RO membranes are so effective at removing contaminants, the water can end up tasting flat. The remineralization cartridge ensures water tastes crisp and refreshing.
5-stage reverse osmosis system configuration
A 5-stage system typically contains the below cartridges. However, like some 4-stage systems, certain 5-stage RO systems may also contain a remineralization cartridge as the final stage.
- Sediment prefilter:A sediment prefilter screens out dirt, sand, rust and other microscopic particles 15 times smaller than a grain of sand.
- Carbon prefilter: An activated carbon prefilter reduces elements that cause water to taste and smell unpleasant, including chlorine.
- 2nd carbon prefilter:Another activated carbon prefilter reduces elements that cause water to taste and smell unpleasant, including the taste and odor of chlorine.
- RO membrane:The reverse osmosis membrane filters out dissolved solids, including radium, lead, arsenic, and many others.
- Polishing filter:The polishing filter is a second activated carbon filter that polishes the water to make sure it's crystal clear.
Below are general recommendations for changing RO system cartridges. If the system you purchase specifies different time intervals, follow your system’s directions.
- Sediment filter – once per year
- Carbon filters – once per year
- RO membrane – once every 2 to 3 years
- Remineralization cartridge – twice per year
Learn more about reverse osmosis: What is a reverse osmosis system and how does it work?
If you have any additional questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.




